介绍
balancer是一个支持http和https的7层负载均衡器,也是一个实现负载均衡算法的go库。
目前支持的负载均衡算法有
round-robinrandompower of 2 random choiceconsistent hashconsistent hash with boundedip-hashleast-load
快速图解
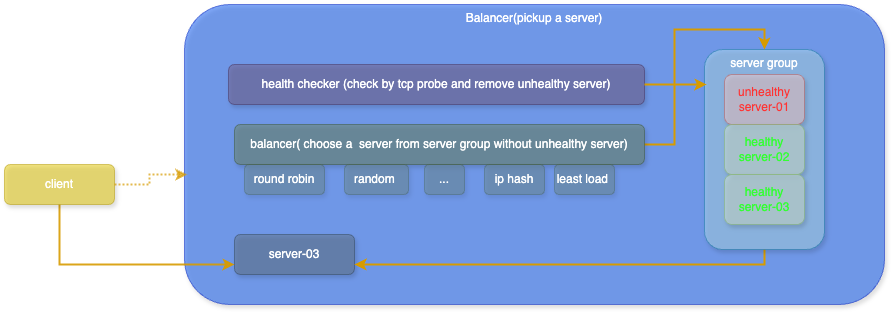
(偷下懒借用张师傅的图片🤣,顺带推荐下 张师傅的tcp小册,讲解的通俗易通,知识点丰富,链接 https://s.juejin.cn/ds/irJbCpd2/)
功能分解
健康检查
负责根据健康检查规则对后端服务进行检查,剔除不健康的节点,加入健康节点
负载均衡
从一组负载均衡节点中根据负载均衡策略选择节点实例
代码赏析
HTTP Proxy 反向代理核心结构
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
type HTTPProxy struct {
// ReverseProxy为原始net.httputil封装的 http/https 代理对象
hostMap map[string]*httputil.ReverseProxy
// 负载均衡对象
lb balancer.Balancer
//用于 保证 alive map 读写安全,因为针对每个单独的节点都会起一个协程 用来读写alive map
sync.RWMutex // protect alive
//用于保存 后端节点健康状态
alive map[string]bool
}路由匹配
因为原生的 HTTP 没有办法动态设置 路由,该项目使用 mux 项目设置路由匹配,当然mux的性能 相较于前缀树差了很多,可以参考下 https://yushuanhsieh.github.io/post/2020-01-21-golang-router ,能够相差几十倍
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
import (
"log"
"net/http"
"strconv"
"github.com/gorilla/mux"
"github.com/zehuamama/balancer/proxy"
)
router := mux.NewRouter()
for _, l := range config.Location {
httpProxy, err := proxy.NewHTTPProxy(l.ProxyPass, l.BalanceMode)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("create proxy error: %s", err)
}
// start health check
if config.HealthCheck {
httpProxy.HealthCheck(config.HealthCheckInterval)
}
router.Handle(l.Pattern, httpProxy)
}
if config.MaxAllowed > 0 {
router.Use(maxAllowedMiddleware(config.MaxAllowed))
}负载均衡策略
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
//负载均衡策略接口
type Balancer interface {
// 新增节点
Add(string)
// 删除节点
Remove(string)
// 选择节点
Balance(string) (string, error)
// 节点新增连接
Inc(string)
// 节点结束连接
Done(string)
}1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
// 定义了默认的 基础负载均衡策略,没有实现任何负载均衡算法,直接单纯实现 balance 接口,具体的算法实现不一定需要实现所有的接口,所以由 BaseBalancer 负责实现默认/空实现接口的功能函数,其他具体的实现只需要引用BaseBalancer即可
type BaseBalancer struct {
sync.RWMutex
hosts []string
}
// Add new host to the balancer
func (b *BaseBalancer) Add(host string) {
b.Lock()
defer b.Unlock()
for _, h := range b.hosts {
if h == host {
return
}
}
b.hosts = append(b.hosts, host)
}
// Remove new host from the balancer
func (b *BaseBalancer) Remove(host string) {
b.Lock()
defer b.Unlock()
for i, h := range b.hosts {
if h == host {
b.hosts = append(b.hosts[:i], b.hosts[i+1:]...)
return
}
}
}
// Balance selects a suitable host according
func (b *BaseBalancer) Balance(key string) (string, error) {
return "", nil
}
// Inc .
func (b *BaseBalancer) Inc(_ string) {}
// Done .
func (b *BaseBalancer) Done(_ string) {}接下来来看几个比较有代表性的负载均衡算法策略
random
策略描述
特点
每次新连接,随机选择一个节点进行处理
代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
// Balance selects a suitable host according
func (r *Random) Balance(_ string) (string, error) {
r.RLock()
defer r.RUnlock()
if len(r.hosts) == 0 {
return "", NoHostError
}
return r.hosts[r.rnd.Intn(len(r.hosts))], nil
}ip-hash
策略描述
根据原ip选择对应的节点
特点
同一客户ip发起的连接在健康检查都ok的情况下,会被分配至同一节点
代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
// Balance selects a suitable host according
func (r *IPHash) Balance(key string) (string, error) {
r.RLock()
defer r.RUnlock()
if len(r.hosts) == 0 {
return "", NoHostError
}
value := crc32.ChecksumIEEE([]byte(key)) % uint32(len(r.hosts))
return r.hosts[value], nil
}least load
策略描述
选择当前处理连接最少的节点
特点
可以根据后端节点的连接处理数量,合理的将新连接配置至后端节点
代码
使用了 FibonacciHeap (斐波那契堆)可以快速排序,获取当前连接数最少的节点,开源库 https://github.com/starwander/GoFibonacciHeap
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
import (
"sync"
fibHeap "github.com/starwander/GoFibonacciHeap"
)
// Tag .
func (h *host) Tag() interface{} { return h.name }
// Key .
func (h *host) Key() float64 { return float64(h.load) }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
// Done refers to the number of connections to the server `-1`
func (l *LeastLoad) Done(hostName string) {
l.Lock()
defer l.Unlock()
if ok := l.heap.GetValue(hostName); ok == nil {
return
}
h := l.heap.GetValue(hostName)
h.(*host).load--
_ = l.heap.DecreaseKeyValue(h)
}健康检查代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
func (h *HTTPProxy) healthCheck(host string, interval uint) {
ticker := time.NewTicker(time.Duration(interval) * time.Second)
/*
当然这里不需要写这个,但是养成良好习惯,及时回收资源,防止泄露
defer func(){
ticker.Stop()
}()
*/
//定时执行健康检查探活逻辑
for range ticker.C {
if !IsBackendAlive(host) && h.ReadAlive(host) {
log.Printf("Site unreachable, remove %s from load balancer.", host)
h.SetAlive(host, false)
h.lb.Remove(host)
} else if IsBackendAlive(host) && !h.ReadAlive(host) {
log.Printf("Site reachable, add %s to load balancer.", host)
h.SetAlive(host, true)
h.lb.Add(host)
}
}
}可以看到就是针对节点的端口进行tcp探活
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
// IsBackendAlive Attempt to establish a tcp connection to determine whether the site is alive
func IsBackendAlive(host string) bool {
addr, err := net.ResolveTCPAddr("tcp", host)
if err != nil {
return false
}
resolveAddr := fmt.Sprintf("%s:%d", addr.IP, addr.Port)
conn, err := net.DialTimeout("tcp", resolveAddr, ConnectionTimeout)
if err != nil {
return false
}
_ = conn.Close()
return true
}可以对比下kubernetes的TCP探活代码对比下
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
//kubernetes tcp端口探活
package probe
import (
"net"
"syscall"
)
// ProbeDialer returns a dialer optimized for probes to avoid lingering sockets on TIME-WAIT state.
// The dialer reduces the TIME-WAIT period to 1 seconds instead of the OS default of 60 seconds.
// Using 1 second instead of 0 because SO_LINGER socket option to 0 causes pending data to be
// discarded and the connection to be aborted with an RST rather than for the pending data to be
// transmitted and the connection closed cleanly with a FIN.
// Ref: https://issues.k8s.io/89898
func ProbeDialer() *net.Dialer {
dialer := &net.Dialer{
Control: func(network, address string, c syscall.RawConn) error {
return c.Control(func(fd uintptr) {
syscall.SetsockoptLinger(int(fd), syscall.SOL_SOCKET, syscall.SO_LINGER, &syscall.Linger{Onoff: 1, Linger: 1})
})
},
}
return dialer
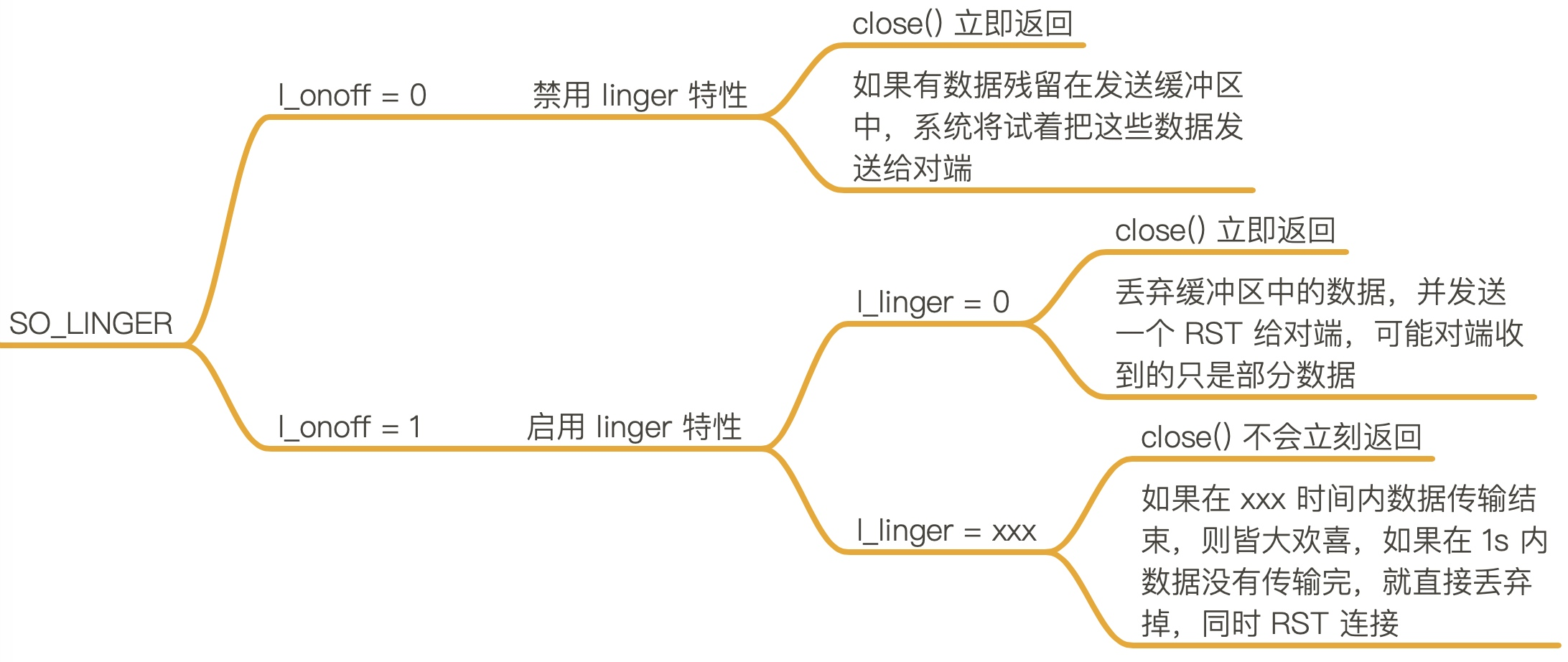
}可以看到 kubernetes 对于http/ tcp 的健康检查进行了特殊处理,开启了 Linger 特性,并设置超时为 1s,在超时后会直接reset连接,相较于默认的timewait是60s,当节点上的kubelet会频繁进行健康检查,很可能会导致很多资源 socket, ephemeral port, conntrack entry 等被占用,这样的话,会导致影响其他请求,相关issue 可以参考
https://github.com/kubernetes/kubernetes/pull/115143
再次感概下 细节决定成败
总结
- 一个基本的负载均衡由 负载均衡算法 和 健康检查组成
- 常见的负载均衡算法有 轮询,iphash,least connect 以及如何编写
- 一个常见的tcp健康检查探针如何编写,已经如何优化http/tcp探测
- linger socket选项 开启后,可以设置 socket.close 的超时时间,如果超过时间,不会进入timewait阶段,会直接reset掉连接
- 斐波那契堆如何在项目中使用
- 常见的路由框架与性能比较

如果你看不到评论,那么就真的看不到评论w(゜Д゜)w